ERP Toolkit
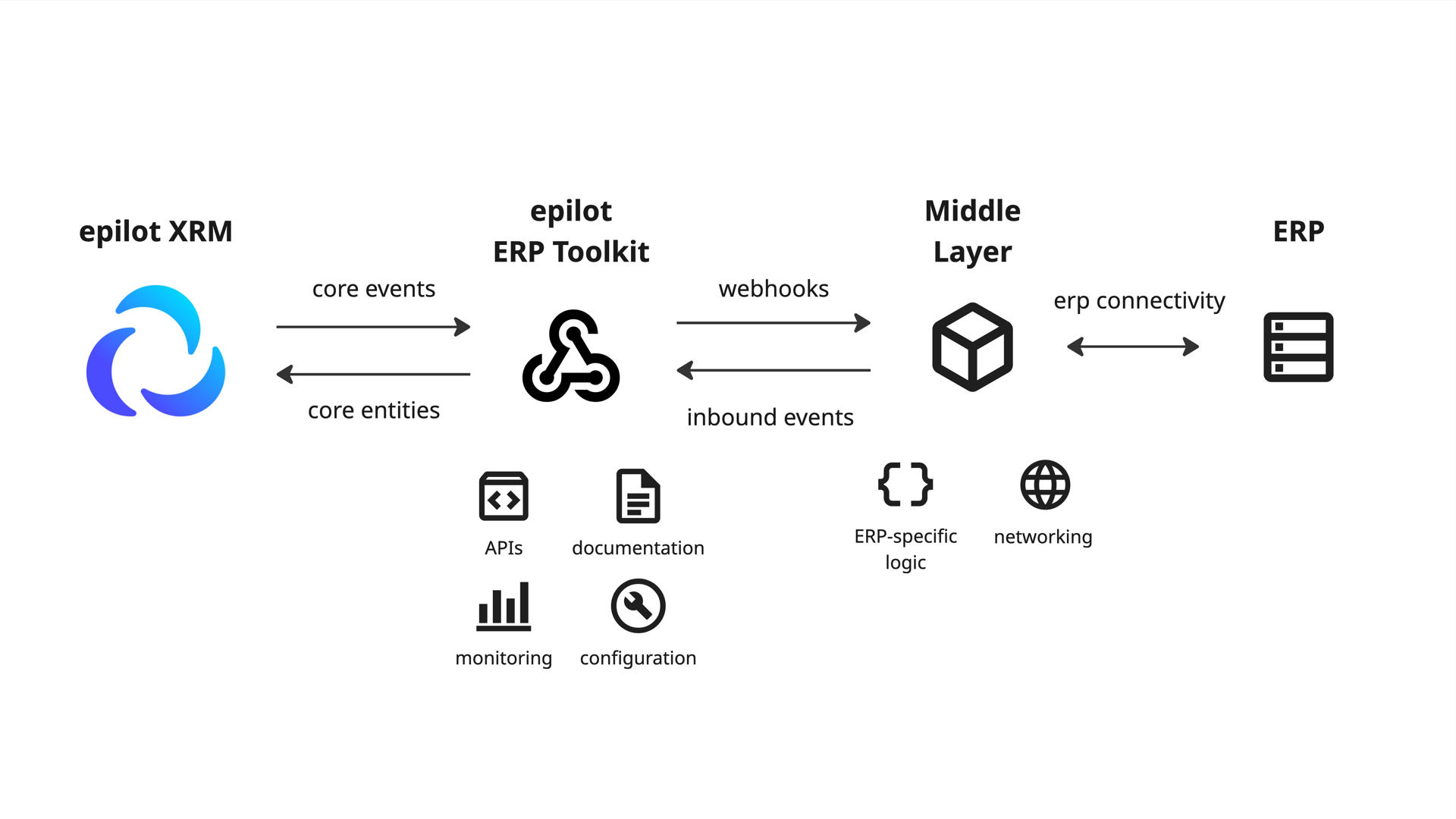
The ERP Toolkit is epilot's opinionated integration platform for building, monitoring, and maintaining ERP integrations. It combines standardized entity and event schemas, JSONata-based mapping, a dedicated inbound ingestion API, configuration APIs, central monitoring, and packaged Blueprints/Apps into a single, cohesive system.
The toolkit is optimized for energy-sector use cases: end-customer self-service via portals, meter reading propagation, contract lifecycle management, and billing account synchronization.
info
The ERP Toolkit does not remove the need for middleware. It standardizes the interface between epilot and your middle layer, radically reducing the complexity compared to direct API integration.
Components
The ERP Toolkit is composed of the following components. Each plays a specific role in the integration lifecycle.
| Component | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Integration Hub | Admin UI in epilot 360 to configure and monitor integrations | In progress |
| ERP Integration API | CRUD API to manage integrations, use cases, and mappings | Stable |
| ERP Inbound API | Dedicated API to receive and simulate inbound ERP events | Stable |
| Use Cases | Documented integration flows with testing support | Stable |
| Core Entities | Standardized entity schemas for mapping targets | Stable |
| Core Events | Standardized event payloads for outbound notifications | Stable |
| Webhooks | Push events from epilot to ERPs via core events | Stable |
| JSONata Mapping | Transformation language for inbound and outbound data | Stable |
| File Proxy | Serve files from external archives on demand without migrating them into epilot | Stable |
| Monitoring and ACKs | Central logging, error tracking, and event replay | In progress |
| Blueprints | Packaged, installable integration setups | Stable |
| Apps | Custom automation actions and portal extensions for ERP logic | In progress |
Integration Hub
The Integration Hub is the administrative UI within epilot 360 (accessible at /app/integrations). It provides a guided wizard for activating ERP integrations, selecting self-service use cases, configuring mappings, running integration tests, and monitoring health.
ERP Integration API
The /v2/integrations CRUD API centralizes all integration configuration in one place:
- Environments -- API URLs, tenant IDs, secrets
- API tokens with scoped roles and permissions
- Inbound use cases with entity mappings
- Outbound use cases with event mappings
- Associated Apps and portal extensions
See the Configuration Guide for API details.
Inbound API
Two dedicated endpoints for receiving ERP data:
| Endpoint | Purpose |
|---|---|
/v3/erp/updates/events | Receive raw ERP data as events for processing |
/v2/erp/updates/mapping_simulation | Dry-run events to verify mappings before going live |
See the Inbound Integration Guide for setup instructions.
Use Cases
A use case is a documented ERP integration flow: a description of how epilot and the ERP work together to implement a specific scenario (e.g., "Keep Contract In Sync" or "Meter Reading Submission"). Each use case defines:
- Which core entities need to be mapped
- Which core events are sent or received
- Expected ERP behavior and response
- Testing via simulated events or webhook test triggers with ACK confirmation
See the Use Cases page for a complete list of inbound and outbound integration flows.
File Proxy
The File Proxy enables epilot to serve files from external document systems (e.g., ERP archives, DMS) on demand. Instead of migrating file content during inbound sync, file entities are created with a custom_download_url pointing to the proxy. When a user views the file, the proxy fetches the document from the external system in real time using a declarative, multi-step HTTP configuration.
JSONata Mapping
JSONata is the core transformation language for defining mappings between epilot's standardized entity/event schemas and ERP-specific data models. It is used across:
- Inbound event processing (ERP to epilot entity mapping)
- Outbound webhook payloads (epilot event to ERP format)
- The Map Data flow building block
Monitoring and ACKs
All inbound and outbound events are centrally logged and surfaced in the Integration Hub. Key capabilities:
- Event replay -- reprocess failed events
- ACK tracking -- ERPs acknowledge processed events via
v1/erp/tracking/acknowledgement, enabling end-to-end visibility - Error alerting -- per-use-case status indicators with actionable error details
- Partner log shipping -- middleware partners can send logs to epilot for centralized monitoring
Architecture
Integration Directions
Inbound (ERP to epilot)
Push data from your ERP into epilot. Typical flows:
- Synchronize customer master data (contacts, accounts)
- Import contracts and subscriptions
- Submit meter readings and consumption data
- Update billing and payment information
Outbound (epilot to ERP)
Push epilot events to your ERP via webhooks. Typical flows:
- New customer registrations and portal sign-ups
- Contract changes (move-in, move-out, termination)
- Self-service requests (IBAN changes, installment adjustments)
- Meter reading submissions
Outbound events use Core Events and are delivered through Webhooks. JSONata transforms simplify payloads before delivery.
Operational Model
The ERP Toolkit and your middle layer have clearly separated responsibilities.
| Toolkit (epilot) | Middle Layer (yours) |
|---|---|
| Stable schemas (core entities/events) and versioning | ERP connectivity (on-prem, VPN, ERP API calls) |
| Deduplication and idempotency | Domain-specific validation required by ERP |
| Inbound ingestion at scale with retries and mapping execution | ACK back to epilot for "processed" state |
| Central monitoring, replay, and retention | |
| Configuration APIs and UI |
tip
Most integrations involve a middleware (e.g., SAP CPI) that handles ERP-specific connectivity and validation. The toolkit standardizes the epilot side so your middleware only needs to speak one protocol.
Integration Patterns
Two primary patterns exist. The right choice depends on your ERP's capabilities.
Event-Driven (Direct)
Your ERP or middleware sends events directly to the ERP Toolkit when data changes.
Best for: systems that support webhooks, need real-time sync, and require minimal transformation beyond mapping configuration.
Pull-Based (Delta Sync with Middleware)
A middleware layer periodically queries your ERP for changes and pushes them to the ERP Toolkit.
Best for: ERPs without webhook support, complex multi-source aggregation, or scenarios requiring custom validation and retry logic.
Comparison table
| Requirement | Event-Driven | Pull-Based |
|---|---|---|
| ERP supports webhooks | Required | Not required |
| Real-time sync needed | Best fit | Depends on polling interval |
| Complex transformations | Limited to mapping config | Full flexibility |
| Custom validation logic | Limited | Full flexibility |
| Aggregating multiple sources | Not supported | Supported |
| Minimal infrastructure | Best fit | Requires middleware |
tip
Many integrations use a hybrid approach: event-driven for simple, real-time updates (e.g., contact changes) and pull-based for complex scenarios (e.g., aggregating invoice data from multiple systems).
Getting Started
- Create an integration -- register your ERP connection via the Configuration API or Integration Hub
- Configure use cases -- define inbound/outbound data flows with entity mappings
- Test mappings -- use the mapping simulation endpoint to validate before going live. See the Mapping Examples repo for a TDD approach
- Send events -- push data from your ERP to the inbound API
- Monitor -- track processing status, errors, and ACKs in the Integration Hub
Continue to the Inbound Integration Guide for step-by-step setup.

