Flexible Entities
The epilot application uses a flexible Entities data layer to model business data on the platform.
Entities
Entities are business objects in epilot with flexible user-defineable schemas.
Each entity can contain arbitrary JSON data, which is made accessible via the Entity API.
Schemas
Schemas are used to define the structure of entities and how they are represented in the UI.
View full List of Schemas page for more info.
Attributes
Schemas define a list of Attributes, which are fields that the entity can have.
These Attributes are rendered in Tables and Details views for all entities of the Schema.
Examples of Attributes:
- First Name
- Last Name
- VAT ID
- Product Name
- Product SKU
- Order ID
Capabilities
Entity Schemas define Capabilities for the entities, which add extra functionality in the entity views.
Some examples of entity capabilities:
- Email Messages
- File Attachments
- Order Item Table
- Workflow Overview
- Automation Actions
Relations
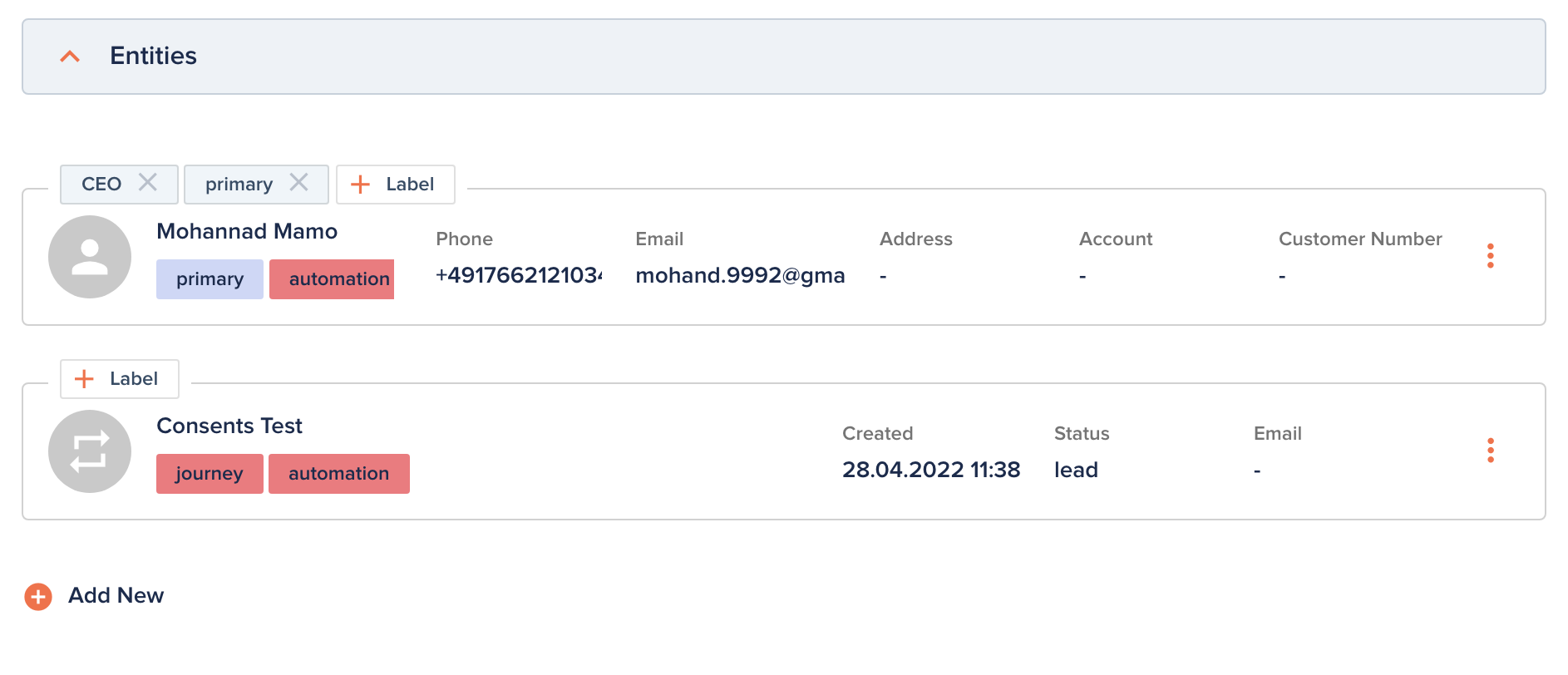
Entities also natively support relations, meaning entities can be linked with each other.
Relations are stored as Relation attributes, containing a reference to the related entity and a list of labels to show on the relation item.
Example relation attribute value:
See Relations for more info.
Activity
Any events related to the entity are stored in an append-only Activity feed.
Each activity item contains a description of the activity, the caller and details about any operations touching the data of the entity.