Taxonomies
[API Docs]
Taxonomies provide a labeling and classification system for organizing entities, relations, and files across the epilot platform. They are managed through the Label Builder in the epilot UI.
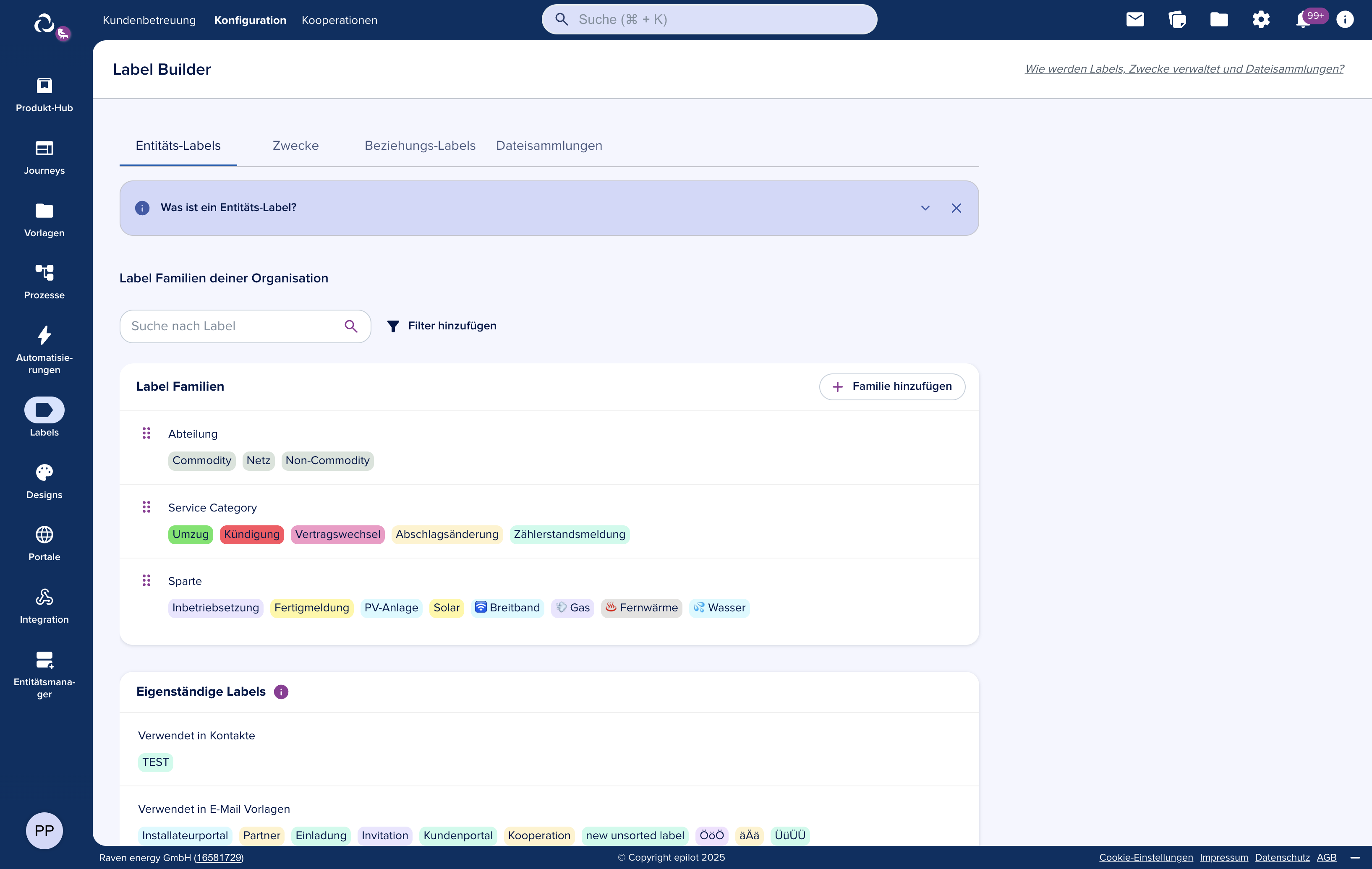
Taxonomy Types
The system supports three taxonomy types, distinguished by slug prefix:
| Type | Prefix | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Entity Labels | _schema_ | Classify entities by business purpose or status |
| Relation Labels | _relation_ | Classify the nature of entity relationships |
| File Collections | _system_ | Organize documents and files into groups |
Entity Labels
Entity labels categorize entities within a schema. Use them to organize by customer type, status, workflow stage, or any business-relevant classification.
System Labels
These built-in labels are locked and cannot be modified. The platform assigns them automatically during certain operations:
| Label | Assigned When |
|---|---|
__hidden | Entity is hidden from standard views |
copy | Entity was duplicated |
merged | Entity resulted from a merge operation |
composite | Entity is a composite (e.g. composite price) |
automation | Entity was created by an automation |
bulk-generated | Entity was created through a bulk operation |
Purposes
Purposes are a standalone taxonomy family (slug: purpose) that define the business intent of an entity. Beyond classification, purposes also control visibility of attributes and attribute groups within the entity detail view.
Relation Labels
Relation labels add context to the links between entities, enabling filtering and business logic based on relationship type.
Predefined Relation Labels
Address relations
_relation_address:billing— Billing address_relation_address:delivery— Delivery address
Account relations
_relation_account:customer— Customer account_relation_account:installer— Installer account_relation_account:planner— Planner account_relation_account:onsite_contact— On-site contact_relation_account:architect— Architect account_relation_account:supplier— Supplier account
Contact relations
_relation_contact:customer— Customer contact_relation_contact:installer— Installer contact_relation_contact:planner— Planner contact_relation_contact:onsite_contact— On-site contact_relation_contact:architect— Architect contact_relation_contact:supplier— Supplier contact
File Collections
File collections organize documents within epilot. Two collection scopes exist:
- Global collections — shared across all users and entities (e.g. company policies, standard contracts)
- User collections — personal to a specific user within a schema context (e.g. working documents)
Working with Taxonomies
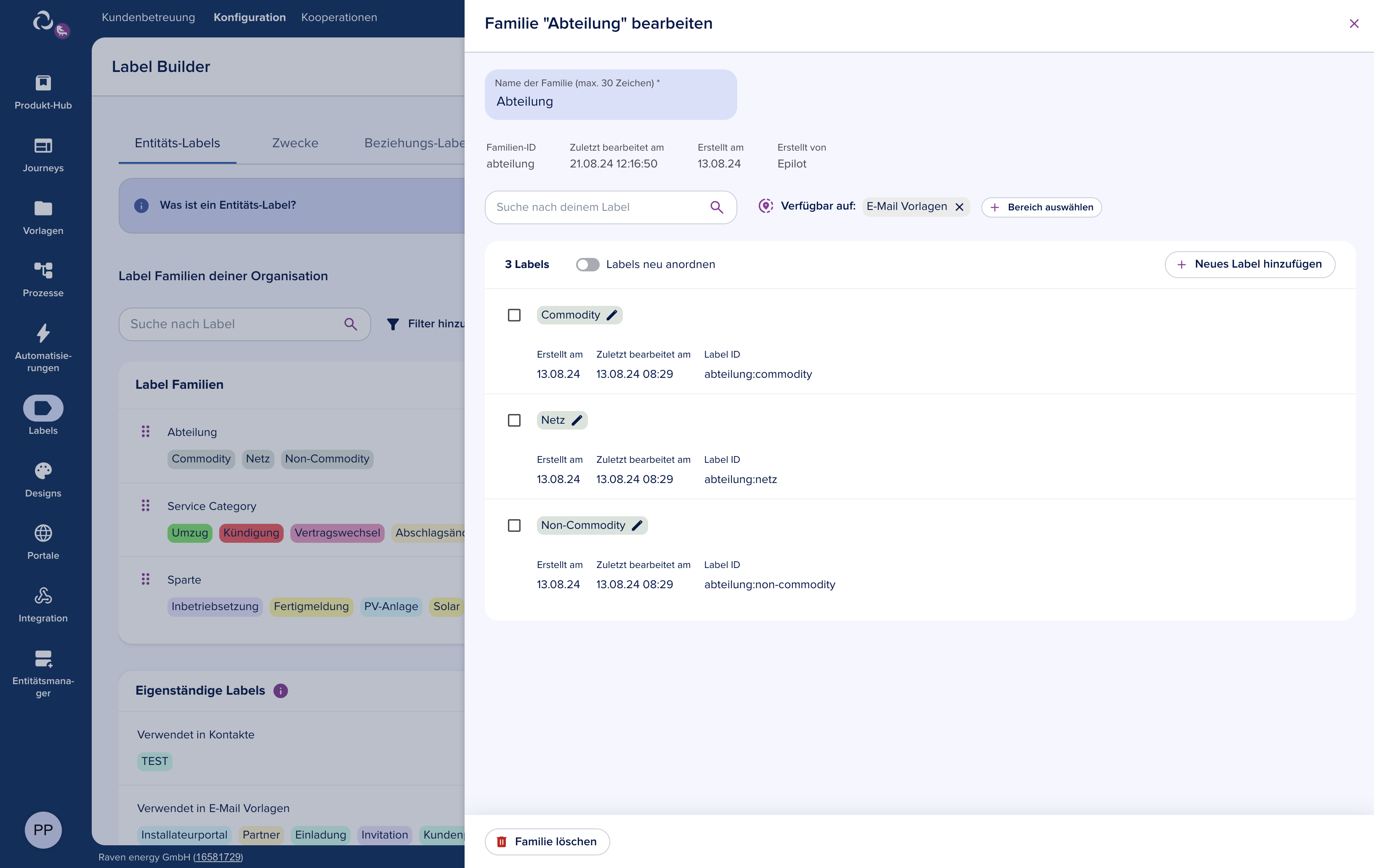
Label Structure
Every taxonomy label has three fields:
{
"id": "uuid",
"slug": "_schema_contact:residential",
"name": "Residential"
}
Permissions
Taxonomy operations require specific permissions:
| Permission | Allows |
|---|---|
label_builder:create | Create taxonomies and classifications |
label_builder:edit | Update existing labels |
label_builder:delete | Delete labels |
Error Handling
| Error | Status | Cause |
|---|---|---|
TaxonomyNotFoundError | 404 | Taxonomy slug does not exist |
TaxonomyAlreadyExistsError | 409 | Taxonomy with this slug already exists |
TaxonomyValidationError | 400 | Invalid request payload |
TaxonomyInUseError | 400 | Cannot delete a taxonomy still in use |
Bulk Operations
Create, update, and delete classifications in a single request:
{
"create": [
{ "id": "uuid", "name": "New Label", "slug": "new-label" }
],
"update": [
{ "id": "existing-id", "name": "Updated Name" }
],
"delete": [
{ "id": "id-to-delete" }
]
}
SDK Example
import { getEntityClient } from '@epilot/entity-client';
const client = getEntityClient();
// Create a taxonomy
const taxonomy = await client.createTaxonomy({}, {
slug: 'project-status',
name: 'Project Status',
type: 'entity',
enabled: true
});
// Add classifications
await client.updateClassifications({
taxonomySlug: 'project-status'
}, {
create: [
{ id: 'uuid-1', name: 'Planning', slug: 'planning' },
{ id: 'uuid-2', name: 'In Progress', slug: 'in-progress' },
{ id: 'uuid-3', name: 'Completed', slug: 'completed' }
]
});
// Search classifications
const results = await client.searchClassifications({
taxonomySlug: 'project-status',
query: 'progress',
include_archived: 'false'
});